Table Of Content

Another type of quasi-experimental design might occur when the researcher doesn't have control over the treatment but studies pre-existing groups after they receive different treatments. There are several types of research study designs, each with its inherent strengths and flaws. The study design used to answer a particular research question depends on the nature of the question and the availability of resources. In this article, which is the first part of a series on “study designs,” we provide an overview of research study designs and their classification. Within-subjects or repeated measures can also refer to an experimental design where an effect emerges over time, and individual responses are measured over time in order to measure this effect as it emerges.
Randomisation
Design method and experimental study of a cathode tool with an extremely high leveling ratio for electrochemical ... - ScienceDirect.com
Design method and experimental study of a cathode tool with an extremely high leveling ratio for electrochemical ....
Posted: Mon, 14 Aug 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
In this design, each participant is exposed to all of the different treatments or conditions, either in a random order or in a predetermined order. This design involves dividing participants into blocks based on a specific characteristic, such as age or gender, and then randomly assigning participants within each block to one of two or more treatment groups. In this design, participants are randomly assigned to one of two or more groups, and each group is exposed to a different treatment or condition. Study designs are the set of methods and procedures used to collect and analyze data in a study.
Overview of methodologies used within a study design
When it's unethical or impractical to assign participants randomly, that’s when a quasi-experimental design comes in. Experimental design is a research method that enables researchers to assess the effect of multiple factors on an outcome. This guide explores the types of experimental design, the steps in designing an experiment, and the advantages and limitations of experimental design. In experimental research, the researcher can control and manipulate the environment of the research, including the predictor variable which can be changed. On the other hand, non-experimental research cannot be controlled or manipulated by the researcher at will. A survey is a tool used to gather relevant data about the characteristics of a population and is one of the most common data collection tools.
Demand characteristics
However, this study design would not be applicable if either of the drugs or interventions overlaps with each other on modes of action or effects, as the results obtained would not attribute to a particular drug or intervention. Clinical trials are also known as therapeutic trials, which involve subjects with disease and are placed in different treatment groups. One of the earliest clinical trial studies was performed by James Lind et al in 1747 on sailors with scurvy.12 Lind divided twelve scorbutic sailors into six groups of two. The group who ate two oranges and one lemon had shown the most sudden and visible clinical effects and were taken back at the end of 6 days as being fit for duty. During Lind's time, this was not accepted but was shown to have similar results when repeated 47 years later in an entire fleet of ships. Based on the above results, in 1795 lemon juice was made a required part of the diet of sailors.
If your research design does not have basic assumptions or postulates, then it is fundamentally flawed and you need to rework on your research framework. Multilevel modeling is used to analyze data that is nested within multiple levels, such as students nested within schools or employees nested within companies. Cluster analysis is used to group similar cases or observations together based on similarities or differences in their characteristics. Physiological measures involve measuring participants’ physiological responses, such as heart rate, blood pressure, or brain activity, using specialized equipment. These measures may be invasive or non-invasive, and may be administered in a laboratory or clinical setting.
They are used in different cases, depending on the type of research being carried out. The changes observed during this period are recorded and evaluated to determine its effectiveness. This process can be carried out using different experimental research methods. Many experiments are carried out in the laboratory, where control can be exerted on the extraneous variables, thereby eliminating them. To him/her, the process of enrolling cases and controls over a period of several months appears prospective.
A Quick Guide to Experimental Design 5 Steps & Examples
If any part of the research design is flawed, it will reflect on the quality of the results derived. SEM is a statistical technique used to model complex relationships between variables. This method involves observing and recording the behavior or phenomenon of interest in real time.
An experimental investigation into whether choice architecture interventions are considered ethical Scientific Reports - Nature.com
An experimental investigation into whether choice architecture interventions are considered ethical Scientific Reports.
Posted: Thu, 26 Oct 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Experimental research is an option when the project includes an independent variable and a desire to understand the relationship between cause and effect. Basically, a researcher can conduct experimental research any time they want to test a theory with variable and dependent controls. This design allows researchers to conduct a similar experiment by assigning subjects to groups based on non-random criteria. When testing a theory or new product, it can be helpful to have a certain level of control and manipulate variables to discover different outcomes. You can use these experiments to determine cause and effect or study variable associations.
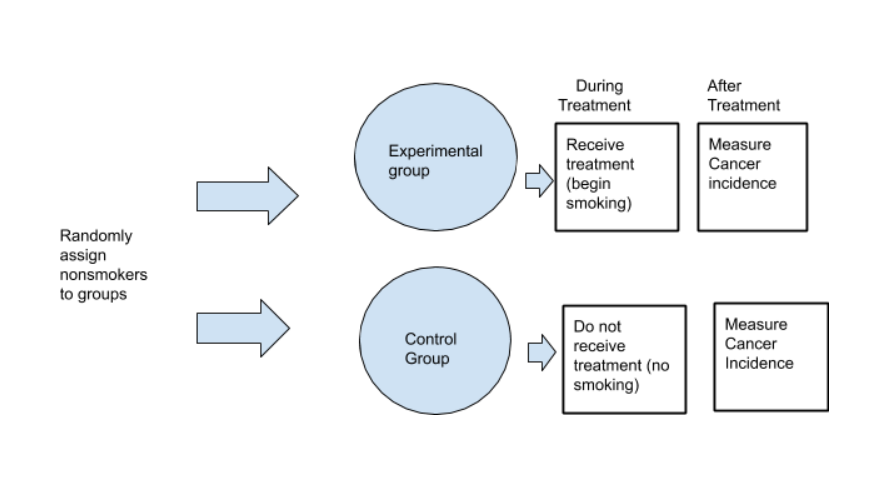
All the groups are post-tested, and the observed differences between the groups are assumed to be a result of the treatment. The experimental research method is widely used in physical and social sciences, psychology, and education. It is based on the comparison between two or more groups with a straightforward logic, which may, however, be difficult to execute. In medical or social research, you might also use matched pairs within your between-subjects design to make sure that each treatment group contains the same variety of test subjects in the same proportions. Each group receives a different level of the treatment (e.g. no phone use, low phone use, high phone use).
Independent variables are not introduced, withdrawn, or manipulated in non-experimental designs, but the same may not be said about experimental research. During the semester, students in a class are lectured on particular courses and an exam is administered at the end of the semester. In this case, the students are the subjects or dependent variables while the lectures are the independent variables treated on the subjects.
This fails to prove if the outcome was truly due to the intervention implemented or due to chance. Cohort studies are typically chosen as a study design when the suspected exposure is known and rare, and the incidence of disease/outcome in the exposure group is suspected to be high. The choice between prospective and retrospective cohort study design would depend on the accuracy and reliability of the past records regarding the exposure/risk factor. In clinical research, our aim is to design a study which would be able to derive a valid and meaningful scientific conclusion using appropriate statistical methods. The conclusions derived from a research study can either improve health care or result in inadvertent harm to patients. Hence, this requires a well‐designed clinical research study that rests on a strong foundation of a detailed methodology and governed by ethical clinical principles.
It allows educators to test new teaching methods and identify what works best. By manipulating variables such as class size, teaching style, and curriculum, researchers can understand how students learn and identify new ways to improve educational outcomes. Experimental research is a powerful tool for understanding cause-and-effect relationships.
Or, at the very least, one must be clear that the terms relate to work flow for each individual study participant, and not to the study as a whole. Experimental designs are a set of procedures that you plan in order to examine the relationship between variables that interest you. The principle of random allocation is to avoid bias in how the experiment is carried out and limit the effects of participant variables.
In this research design, an independent variable is manipulated, but the participants of a group are not randomly assigned. This type of research design is used in field settings where random assignment is either irrelevant or not required. Based on the direction of inquiry, study designs may be classified as forward-direction or backward-direction. In forward-direction studies, the researcher starts with determining the exposure to a risk factor and then assesses whether the outcome occurs at a future time point.
Factor analysis is used to identify underlying factors or dimensions in a set of variables. This can be used to reduce the complexity of the data and identify patterns in the data. Descriptive statistics are used to summarize and describe the data collected in the study. This includes measures such as mean, median, mode, range, and standard deviation.

No comments:
Post a Comment